 Investment in stock markets is not limited to investing in pure stocks. It has an ocean of investing opportunities but primarily these investments are mostly categorised into equity and debt instruments. The equity and debt markets present a diverse class of investments that have their own set of pros and cons. Discussed hereunder is the meaning of equity and debt markets and the primary differences between the two. Read More: Relationship between macroeconomic factors and Indian stock markets
Investment in stock markets is not limited to investing in pure stocks. It has an ocean of investing opportunities but primarily these investments are mostly categorised into equity and debt instruments. The equity and debt markets present a diverse class of investments that have their own set of pros and cons. Discussed hereunder is the meaning of equity and debt markets and the primary differences between the two. Read More: Relationship between macroeconomic factors and Indian stock markets
 Equity markets are the platform to buy and sell shares of public limited companies, i.e., companies listed on stock exchanges. Shares are available for the public subscription initially through the company’s IPO (Initial Public Offer) and then through open market trading. Equity markets can be classified into primary markets and secondary markets. The former is where shares of a company are offered to the public through IPO or FPO. on the other hand, the secondary market is where investors and traders can buy stocks other than from the IPO or FPO route. This secondary market is also referred to as the derivative market where investors can trade in futures and options, forward contracts, etc. which derive their value from the underlying assets (stocks). Equity markets are highly volatile but have the potential to provide the highest returns in the long term. The types of trades in the equity markets include intraday traders, position trading, and BTST (Buy Today and Sell Tomorrow).
Equity markets are the platform to buy and sell shares of public limited companies, i.e., companies listed on stock exchanges. Shares are available for the public subscription initially through the company’s IPO (Initial Public Offer) and then through open market trading. Equity markets can be classified into primary markets and secondary markets. The former is where shares of a company are offered to the public through IPO or FPO. on the other hand, the secondary market is where investors and traders can buy stocks other than from the IPO or FPO route. This secondary market is also referred to as the derivative market where investors can trade in futures and options, forward contracts, etc. which derive their value from the underlying assets (stocks). Equity markets are highly volatile but have the potential to provide the highest returns in the long term. The types of trades in the equity markets include intraday traders, position trading, and BTST (Buy Today and Sell Tomorrow).
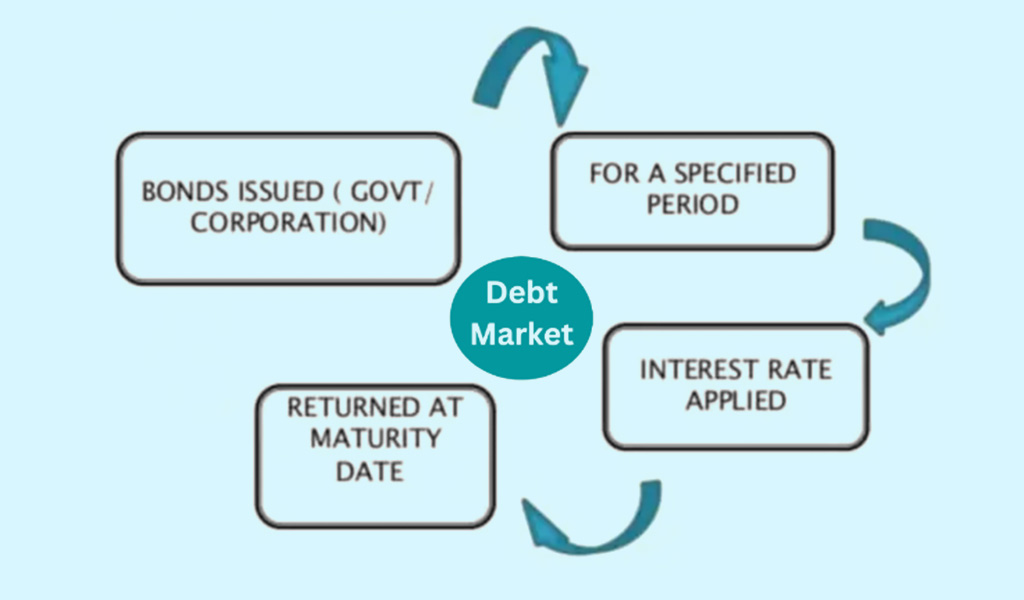 Similar to equity markets, debt markets are the platform where investors can buy and sell various types of debt instruments. Debt instruments are in the form of loans provided by the investors to the debt issuers and they get returns in the form of fixed interest on these instruments. Debt markets are also classified into primary and secondary markets where investors can directly subscribe to the debt instruments from the issuers of such instruments in the primary markets. Secondary markets cater to investors who want to invest in debt instruments but did not get a chance to do so at the time of their issue. Liquidity is therefore the key feature of the secondary markets. The types of instruments available in the debt markets include corporate bonds, government bonds, municipal bonds, mortgage-backed securities, and asset-backed securities.
Similar to equity markets, debt markets are the platform where investors can buy and sell various types of debt instruments. Debt instruments are in the form of loans provided by the investors to the debt issuers and they get returns in the form of fixed interest on these instruments. Debt markets are also classified into primary and secondary markets where investors can directly subscribe to the debt instruments from the issuers of such instruments in the primary markets. Secondary markets cater to investors who want to invest in debt instruments but did not get a chance to do so at the time of their issue. Liquidity is therefore the key feature of the secondary markets. The types of instruments available in the debt markets include corporate bonds, government bonds, municipal bonds, mortgage-backed securities, and asset-backed securities.
The key differences between equity markets and debt markets are highlighted below.
| Category | Equity Markets | Debt Markets |
|---|---|---|
| Ownership | Investors buying shares in a company through equity markets have the right to ownership of a portion of the company. | Investors in debt instruments lend money to the issuers of such instruments and become creditors. They do not get any ownership similar to investment in shares. |
| Risk | Equity markets are highly volatile and have the highest risk of investment | Debt markets are considered to be stable and less volatile. |
| Returns | Similar to the high risk of the equity markets, the corresponding returns from equity instruments are also higher but are quieter fluctuating and may not be a good source of a steady source of income. | Debt instruments do not usually provide high returns similar to equity instruments but such returns are quite a stable source of fixed income for investors. |
| Issuers | The issuers of the equity instruments are the companies that issue shares. | Issuers of the debt securities are the companies and government |
| Regulators | Equity markets are regulated by SEBI. | Debt markets are regulated by SEBI and RBI. |
| Taxation | Income from the equity market can be in the form of dividends and capital gains. Dividends are taxable in the hands of the investors at applicable slab rates. STCG and LTCG on equity instruments are taxed at 15% and 10% respectively. Investors get an exemption in the case of LTCG for net gains up to Rs. 1,00,000. | Income from the equity market can be in the form of interest and Capital Gains. Interest and STCG are taxable in the hands of the investors at applicable slab rates. LTCG on debt instruments is taxed at 20% after giving the benefit of indexation. |
The pros and cons of investing in equity and debt markets are highlighted below.
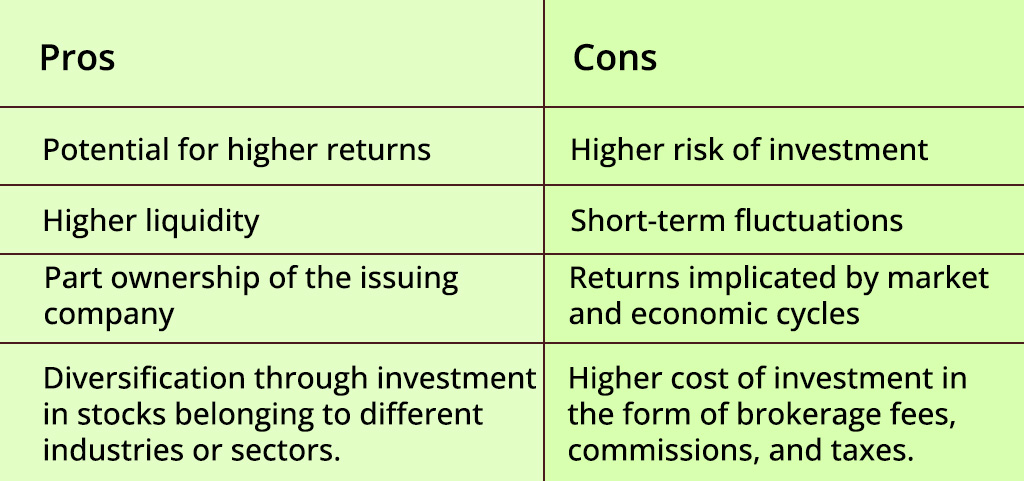
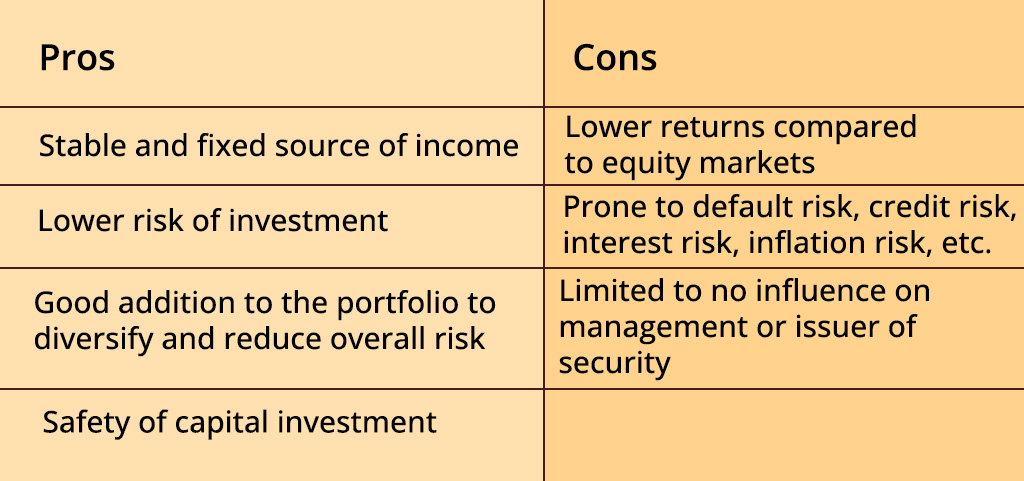
Equity markets and debt markets both provide ample investment opportunities for the investors based on their risk perception and returns expectations. The tenure of investment is another important factor that influences the investment decision between equity markets and debt markets. Investors need to thoroughly understand the differences between equity and debt markets to make optimum investment decisions an create a healthy investment portfolio that meets their financial goals in the most optimum manner.

The Japanese Yen (JPY) has long been one of the world’s major currencies, ...

The Russian-Ukraine war is in its 9th month which seemed most unexpected in the ...

The term "market" can have several exclusive meanings; however, it's used mostl...